CAUSAL MODEL OF FACTORS EFFECTING ON RAJAMANGALA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY COUNCIL ROLES
ดร.ปกรณ์ ลวกุล
Dr.Pakorn Lawakul
(บทความชิ้นนี้เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของการศึกษาระดับปริญญาเอก ครุศาสตร์อุตสาหกรรมดุษฏีบัณฑิต สาขาการบริหารอาชีวศึกษา สถาบันเทคโนโลยีเจ้าคุณทหารลาดกระบัง ของ ดร.ปกรณ์ ลวกุล ได้รับการตอบรับให้ตีพิมพ์เป็นภาษาอังกฤษ ในวารสารครุศาสตร์ คณะครุศาสตร์ จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย ปีที่ 41 ฉบับที่ 3 เดือน กรกฎาคม – กันยายน 2556)
บทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อพัฒนาโมเดลปัจจัยเชิงสาเหตุที่ส่งผลต่อบทบาทหน้าที่ของสภามหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคล โดยใช้กรอบแนวคิดจากบทบาทหน้าที่ของสภามหาวิทยาลัยตามพระราชบัญญัติมหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคล พ.ศ.๒๕๔๘ กลุ่มตัวอย่างเป็นผู้บริหารมหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคล ประกอบด้วย กรรมการสภามหาวิทยาลัย กรรมการสภาคณาจารย์และข้าราชการ และผู้บริหารตั้งแต่ระดับรองคณบดีขึ้นไป จำนวนทั้งสิ้น ๓๗๔ คน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัยประกอบด้วย แบบสอบถามความคิดเห็น การวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลใช้โปรแกรม SPSS ในการหาค่าสถิติพื้นฐาน และการใช้โปรแกรม LISREL ๘.๗๒ ในการวิเคระห์ความตรงเชิงโครงสร้างของโมเดลปัจจัยเชิงสาเหตุ
ผลการวิจัยพบว่า โมเดลปัจจัยเชิงสาเหตุที่ส่งผลต่อบทบาทหน้าที่ของสภามหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคลมีความสอดคล้องกับข้อมูลเชิงประจักษ์อยู่ในเกณฑ์ดี โดยพิจารณาจาก ค่าไค-สแควร์เท่ากับ ๑.๑๔๓ ที่องศาอิสระเท่ากับ ๑๒๔ ดัชนี GFI เท่ากับ ๐.๙๒ ดัชนี AGFI เท่ากับ ๐.๘๗ ค่า Standardizer RMR เท่ากับ ๐.๐๒๗ และค่า RMSEA เท่ากับ ๐.๐๔๘ ตัวแปรที่มีอิทธิพลทางตรงต่อบทบาทหน้าที่ของสภามหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคล ได้แก่ ภาวะผู้นำ เครือข่ายความร่วมมือ โครงสร้าง ภูมิหลัง และระบบบริหาร
ABSTRACT
This research aimed to develop a causal model of factors effecting the role of the university council of Rajamangala Universities of Technology. The researchers have studied and built framework for the research on roles and duties of Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council according to Rajamangala University of Technology Act of BE. 2005. The samples consisted of the Rajamangala University of Technology Councils, Council staff, officials, and executives (vice dean level or above), totaling 374 people. The research tool was questionnaire. The findings were processed by analyzing the statistical basis with SPSS and the correlation structure of the causal model with LISREL 8.72.
The results showed that Modeling Factors Affecting the Roles of the Council were in accordance with the empirical data, by considering Chi-square of 1.143 at degree of freedom of 124, GFI of 0.92 and AFGI of 0.87, Standardized RMR of 0.027 and RMSEA of 0.048. The factors directly affecting roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council were leadership, cooperation network, structure, background, and management system.
Key words: roles and duties, university council, causal model of factors
Introduction
University is the highest educational institution producing human resources that affect future planning of the country. University is an important part to create knowledge-base and innovation of society that is the main alternative for young people that will drive and elevate quality of context of expansion as required by society. Both Thai and international higher education management have defined the highest level organization in university that many countries value university as price of society. Investment in university can be compared to investment for the country’s future. The organization of the supreme level in university is like government of the university to take charge of finance, treasury, society and stakeholders of the university in decision making process about all of the university’s policies. (Moses, 2006)
The Second 15-Year Long Term Higher Educational Framework (2008-2022) has paid attention to Governance and Management that is an important factor that directly affects development of universities and higher education institutions. Organization in supreme level which is university council plays an important role and is responsible for growth and productivity of the university according to its missions (Office of the Higher Education Commission, 2007) in terms of academic, research, academic service to society and culture nourishing (Knowledge Network Institute of Thailand, 2010). Members of university council who are members of the organization have, therefore, important roles to drive the university as prescribed by their roles in terms of policy making, regulation issuing, monitoring, supervising and assessing, considering for further action and for approval and supporting the university’s work. At present, most of power exercised by the council lacks efficiency because 1) structure of the university does not comply with governance principle 2) the council work as prescribed by job description is not in supervising or monitoring and determining policy style 3) Thai culture focuses on compromising 4) some members of the council do not have good understanding in roles and duties in higher education 5) there is lack of complete and clear information technology for management, decision making and aggressive working style 6) the council is group of people working on meeting basis so it needs a unit to support the council’s work to be working mechanism (Chaweewan Limwattana, 2010). Moreover, efficiency of the council members has several linking issues such as 1) size of the council 2) composition of the council 3) recruitment and response process 4) culture and meeting style 5) administrative and strategic agenda 6) roles of the members 7) required sub-committee 8) relationship between the council directors and rectors 9) linkage of the council with external units and 10) duties of Secretary of the University Council (Kririt Bunyakiart, 2010).
Rajamangala University of Technology was formerly educational institution in vocational level originated from combination of 35 colleges under Department of Vocational Education both in central and regional areas all over the country in 1975. It was first established as Technology and Vocational College with main purpose to provide bachelor degree program. Later in 1988, the institution’s name was changed to Rajamangala Institute of Technology and in 2005, Rajamangala University of Technology Act of BE. 2005 was enacted with reasons that it was suitable to found 9 Rajamangala Universities of Technology to replace Rajamangala Institute of Technology in order to serve as the governmental high educational institutes to provide advanced vocational education focusing on practice, teaching, research, producing professional teachers, provision of science and technology knowledge and nourishing arts and culture. It mainly focuses on vocational graduates to pursue professional study in bachelor level (Royal Gazette, 2005). As a result, the 9 newly-established universities all over the country have educational context developed from vocational education institutes to universities specialized in providing science and technology education. Moreover, all the 9 universities are obliged to have its own university council with the same number of directors, selection method, qualifications, authority and duties of the directors (Royal Gazette, 2005).
From having vocational education with several campuses to be one university for all the 9 universities, the highest level administration body for all the 9 universities which is university council has very important roles in administering the universities. Moreover, context of the 9 universities has different dimensions such as quantitative dimension on difference in number of units under supervision, location dimension which is difference in location in central area and regional area and management dimension that is difference in roles of the units. However, they are under the same regulation on university council. The researchers, therefore, have interested in conducting a research on university council with the use of case study of Rajamangala University of Technology to build causal factor model effecting roles and duties of the university councils.
Objectives of the Research
1. To develop causal factor model affecting roles and duties of the university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology.
2. To verify compliance of the causal factor model affecting roles and duties of university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology and empirical data.
Research Framework
For the causal factor model affecting roles and duties of university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology, the researchers have studied and built framework for the research on roles and duties of Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council according to Rajamangala University of Technology Act of BE. 2005 (Royal Gazette, 2005) as follows:
1. Policy setting and regulation issuing
2. Governing, monitoring and assessing
3. Considering for further action and approval
4. Supporting work of the universities
For the causal factor model affecting roles and duties of university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology, the researchers have synthesized ideas of Moses (2006) , Fielden (2008), Watana Luanglue (1995) and Phranakhon Rajabhat University (2007) and focus group (DRLE ,2010). The researchers have summarized the ideas as framework for the research as 1. Leadership 2. Background of Directors 3. Structure of the Council 4. Council management 5. Corporate culture of the Council and 6. Cooperation network.
Chart 1: Framework of causal factor model effecting roles and duties of university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology
Assumption
The causal factor model effecting roles and duties of university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology developed by the researchers is in line with empirical data.
Research Methodology
The researchers have employed Research and Development procedures with 2 steps of research as follows:
Step 1: Development of causal factor model affecting roles and duties of university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology by analyzing and holding group discussion
Step 2: Verification of compliance and analysis of causal influence nature of the causal factor model affecting roles and duties of university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology with empirical data.
1. Population and Sample
Population of the research is the management comprising 270 directors of the 9 Rajamangala Universities of Technology with 30 each, 180 directors of Lecturer Council and government officers from the 9 institutions with 20 each and management at the level of Deputy-Dean and Deputy-Director and over of the 9 universities. The management is from 118 units with 4 persons each (Ministerial Regulation, 2006) which totally makes 472 persons. The total population is, therefore, 922 people.
Sample of the research is the management comprising directors of the University Council, directors of Lecturer Council and government officers from the 9 universities. Moreover, it includes management in Deputy-Dean and Deputy-Director level and over from 118 units of the 9 universities. The sample is selected by Stratified Random Sampling and size is set by Yamane Table (Pannee Leekitwatana, 2005) at confidence level of 95% and error of 0.04 with sample size of 372. The data was analyzed by Lisrel with sample size criteria per observed variable of 10-20 times (Hair, et al., 1998; Wiratchai, 1999 cited in Limchumroon and Lawthong, 2009).
2. Research Tool
The tool for the research is questionnaire divided into 2 parts as
Part 1 6 questions on general condition of the sample provided as check list
Part 2 Questions to survey causal factors affecting roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council provided as rating with 5 levels with confidence level of 0.92.
Data Analysis
1. Analyze general information of the samples with the use of descriptive statistics and factor analysis to extract compositions of the variables by SPSS.
2. Confirmatory factory analysis with the use of Lisrel to verify compliance of the model. The statistics and criteria used for the analysis with the empirical model (Nonglak Wiratchai, 1999; Supamas Angsuchote et al., 2008; Joreskog and Sorbom, 1993) are as follows:
1) Chi-square per degree of freedom is less than 2.
2) Goodness of fit index : GFI is close to 1.
3) Adjusted goodness of fit index : AGFI is close to 1.
4) Root mean square residual : RMR is close to 1.
Research Findings
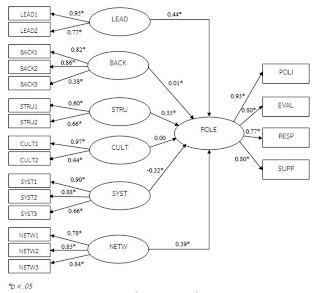
The research on the causal factor model effecting roles and duties of university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology indicates that in overall picture, the model under the assumption complies with the empirical data in good level (Supamas Angsuchote, 2008) considering Chi-square of 1.143 at degree of freedom of 124. The GFI is 0.92 and AFGI is 0.87 while the Standardizer RMR is 0.027 and RMSEA is 0.048. The factors directly affecting roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council are leadership, cooperation network and management system.
Chart 2: Revised Causal Factor Model Effecting Roles and Duties of Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council
From the causal factor model affecting roles and duties of Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council, it can be explained as follows:
1. Leadership of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council members directly influences roles and duties of the council with influence size of 0.44 (at significance level of 0.05). Therefore, the directors of the council who have leadership will perform their duties well.
2. Background of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council members directly influences roles and duties of the council with influence size of 0.01 (at significance level of 0.05). Therefore, the directors of the council who have background will perform their duties well.
3. Structure of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council members directly influences roles and duties of the council with influence size of 0.35 (at significance level of 0.05). Therefore, the structure of the council will contribute to their duties.
4. Management system of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council directly influences roles and duties of the council with influence size of -0.32 (at significance level of 0.05). Therefore, good management system of the council will contribute to their duties.
5. Corporate culture of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council does not directly influence roles and duties of the council (at significance level of 0.05). Therefore, the corporate culture of the council does not affect their duties.
6. Cooperation network has direct influence on roles and duties of the council with influence size of -0.39 (at significance level of 0.05). Therefore, cooperation network of the council will contribute to performing their duties well.
The above research result leads to the conclusion that the degree of performance efficiency of the council members depends on several factors that is in line with assumption of the researchers. There are 5 factors directly influencing roles and duties of the council as leadership, cooperation network, structure, background and management system.
Result Discussion
From the causal factor model effecting roles and duties of Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council according to the research assumption, it is found that the model is in line with the empirical data which can be discussed as follows:
1. Leadership of the directors of the university council has direct influence on roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council in positive direction. It means that if the directors have high leadership, they will be able to perform their duties well. When they have leadership in working and meeting for making decision for policy setting and regulation issuing, considering for further action and approval, governing, monitoring and assessing or promoting and supporting the university’s work, they will do their work well and the overall picture of cooperation to be in a direction that is beneficial for the university. Maturity and leadership of the members have greatly contributed to decision making of the council since it is the highest level administration body that must be able to make a decision by their personal and group judgment to produce academic creativity and support activities that is in line with the policy. This complies with the research of Kiatkamjorn Kuson (2006) stating that leadership means process in which an individual is able to motivate other people to cooperate to efficiently achieve target. The leader must possess traits that are appropriate in terms of knowledge, ability, wisdom, vision and fairness by holding principle for management, responsibility and understanding colleagues as human being. Leadership is an important composition for every organization that needs development. Lack of this may result in inefficiency of the organization. Leaders have different roles depending on objectives of work or activities, problems and situations and relevant groups that is in line with the concept of Fiedler (1976) that explained that efficient leadership depends on compliance between the leader and relevant situation.
2. Background of the directors of the university council has direct influence on roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council in positive direction. This means that background in experience in educational management, organization management and academic title of the council members will complement good performance. If the members of the council have knowledge, maturity, high education level and experience, they will be able to perform their duties well as defined by workload of the university council that is in compliance with the research of Papalia & Olds (1985) which mentions that background is one of important factors that reflect behaviors of human beings that are both visible and invisible or unnoticeable. Individual background will reflect different personality since it is past experience that is socialization accumulated for years so they become attitude, belief and value portrayed by positive and negative behaviors. These may lead to appropriate and inappropriate personality that is in line with research of Tierney, Kezar and Minor (2008) who conducted research on selection and appointment of the directors to administer colleges and universities in government sector and summarized that source and background of each director that the administration committee is very crucial for the institutions since they will lead and develop the institutions to better goals. Therefore, good back ground is required. Research of Sanoh Piantanyakorn (1995) has summarized nature and source of the external honorable directors of the council that they will contribute to the university more than those from internal source. It is found that the honorable and external directors will have characteristics as 1) being highest level management of the agency with which the university has to closely coordinate such as Secretary-General of Office of the Education Council, Permanent Secretary of Ministry of University Affairs and Director-General 2) honorable or specialists in fields taught in that university 3) persons having important roles in defining and suggesting need in graduates such as bankers and owners of big companies.
3. Structure of the council has direct influence on roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council in positive direction. This means that appropriate structure will contribute to efficiency in performance which follows research conducted by Moses (2007) that composition of each university council structure is different from country to country and university to university. It has also changed over time but the principle is to have sufficient number of members and to do the university management efficiently for good governance, responsibility and competitiveness with other domestic and international institutes. The members must be strong and can be elected or appointed. They can be internal and external people who have and do not have voting right. This is in accordance with Watana Luanglue (1995) who studied about categorization of performance indicators of Thai university councils. He found that council of small university is more efficient than that of the middle and large counterparts in every dimension which is institute context understanding dimension, information learning dimension, group working dimension, participative dimension, university work support dimension, problem analysis and decision making dimension, monitoring and assessment dimension and strategy setting dimension.
4. Corporate culture of the university council does not have direct influence on the roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council. It means that the corporate culture does not affect performance of the council members. This may be because context of corporate culture of Thai universities may not be in line with that of foreign universities which complies with Bodi Treesukon (2012) who found that creating corporate culture is a difficult task since it is related to value, belief, norm and behavior of people in the organization. The corporate culture may not be concrete and tangible but is underwater wave driving change or adjustment or failure of the organization. Corporate culture creation process must be considered since if it is virtuous process, it will create productive behavior. In contrast, destructive process may lead to dysfunctional behavior. And there is no success formula for the creation that any organization can adopt.
5. Management system of the council has direct influence on duties and roles of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council in positive direction. This means that good management system of the council will complement good performance of the members. This conforms to research by Moses (2008) who summarized that regardless of source or selection method, the council members must act for best interest of the university and not for interest of their groups and they are not representative of their group. It is responsibility toward the university not their group. Members of the university council must be responsible for their duties for highest interest of the university together and they have to work and bear responsibility as a whole. There are 2 ways of council management as 1) Council and 2) Board of Directors. Those who work in council-style will be aware that the duty is to attend meetings as representatives of stakeholders such as lecturers, students, employees, alumni, community and government representatives to supervise policy, target, direction, strategy, and finance of the university. For those in Board of Director-style, they will work as a group and are not representatives of their groups. They will be one group although each person is selected by different methods. Moreover, there will always be honorable committee members as Professional Board of Directors who understand the principle of Board of Directors and they will possess professional skill that doing this work requires understanding and skill to be able to take charge of the work. It is estimated that the Board of Directors-style will become more popular.
6. Cooperation network of the council has direct influence on duties and roles of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council in positive direction. This means that good cooperation network of the council will complement good performance of the members. This is in line with the focus group (DRLE, 2010) that concluded that Rajamangala Universities of Technology are newly established that need cooperation network among the 9 universities, other universities and universities in international level following theory Croewther. According to Croewther (1996), cooperation is key factor for achievement of teamwork. So it is desirable for team or group or organization which means working with other people, cooperating, brainstorming and working with others to create something together.
Recommendations
Recommendations for research findings application
1. Leadership of the university council members is the most important direct variable to performance of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council. Therefore, acquisition of the members should consider leadership especially that of the President and leadership in terms of policy, governing and promoting and supporting the university’s work.
2. Cooperation network is the second important direct variable to performance of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council next to leadership. Therefore, acquisition of the members should consider promotion of the council to create more cooperation network especially that among the 9 Rajamangala Universities of Technology, with other universities and cooperation in international level.
3. Structure of the university council is the third important direct variable to performance of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council next to leadership and cooperation network. Therefore, setting of the council structure should consider relevant factors such as number of members, recruitment process of the President and members and term of service.
Recommendations for the next research
1. There should be qualitative research on causal factors affecting roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council to find in dept information of the performance of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council.
2. There should be research on intervening variable to study influence of direct and indirect influence of roles and duties of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council in order to get information on information technology of the Rajamangala Universities of Technology Council.
Summary
The causal factor model effecting roles and duties of the university councils of Rajamangala Universities of Technology comprises leadership, background, structure, management system and cooperation network.
Bibliography
Act of Rajamangala University of technology. 2005. Government Gazette. Volume 112 Section 6 A. 24-25.
Kririt Bunyakiart. 2010. Efficient Performance of University Council Members. Documents for Seminar on Good Governance and Management System in Rajamangala Universities of Technology, Bangkok 19 October. (Photocopy)
Kiatkamjorn Kuson. 2000. “Causal Factor Model of Factors Affecting Leadership of Deans of Government High Education Institutes under Ministry of University Affairs” PhD. Thesis Chulalongkorn University.
Chaweewan Limwattana. 2010. Development of Role Model Office of Government University Council in Thailand. Documents for Seminar of Knowledge Network Institute of Thailand at Infinity 1, Pullman King Power, Bangkok. 1 July. (Photocopy)
Nonglak Wiratchai. (1999). LISREL Model: Analytic Statistics for Research. 3rd Printing. Bangkok : Chulalongkorn University Press.
Bodi Treesukon. 2012. Corporate Culture Building Strategy. [online]. Available : www.sbdc.co.th/filedownload/culture_total.pdf
Pannee Leekitwatana. 2005. Research Methodology. Bangkok: Paytai Printing. 94.
Phranakhon Rajabhat University. 2007. Roles of Thai University Council. International Conference on “Quality Control of University” 22-23 June 2007. 139-147)
Watana Luanglue. 1995. “Performance Indicator of Thai University Council” PhD. Thesis Chulalongkorn University.
Supamas Angsuchote et al. (2008). Statistics for Research on Social and Behavioral Sciences :Technique for Use of LISREL. Bangkok : Mission Media.
Office of the Higher Education Commission, Ministry of Education. 2007. 15-Year High Education Framework, No. 2 ( Year 2008-2022). (Photocopy)
Knowledge Network Institute of Thailand. 2010. Establishment of University Council Office. Documents for Seminar of Knowledge Network Institute of Thailand at Infinity 1, Pullman King Power, Bangkok. 1 July. (Photocopy)
Sanoh Piantanyakorn. 1988. “Analysis of Thai High Education Institute Organization Chart ” PhD. Thesis Chulalongkorn University.
Sanoh Tiyao. 2001. Management Principle. Bangkok: Thammasat University. 47
Supamas Angsuchote. 2008. Statistics for Research on Social and Behavioral Sciences :Technique for Use of LISREL. Bangkok. Mission Media.
Adrianna Kezar, William G. Tierney, 2006. 7 Elements of Effective Public-Sector Boards. Association of Governing Boards of Universities and Colleges, Trusteeship. (Nov-Dec 2006) 14(6) : 4
Crowther, J. 1996. Oxford Advanced Learner’ Dictionary. 5th ed. NY: Oxford University.
DRLE 2010. 2010. International Conference on Developing Real-Life Learning Experiences : Innovation and Technology Education 27 August 2010. KMITL.
Ingrid Moses . 2006. ‘Global Trends in University Governance’ Thai-Australian Workshop on University Governance Bangkok, 22-23 June 2006.
John Fielden. 2008. Global Trends in University Governance. Washington, D.C. The World Bank.
Joreskog, K.G. and Sorbom, D. (1993). LISREL 8 : User’s Reference guide. Chicago : Scientific Software International.
Ministerial Regulation.2006. Government Gazette. Volume 123 Section 118 A. 9-35
Papalia, D. D., & Olds, S. W. 1985. Psychology. New York. McGraw-Hill.
William G. Tierney, Adrianna Kezar, and James T. Minor. 2008. Selection and Appointment of Trustees to Public College and University Boards. Center for Higher Education Policy Analysis(CHEPA). [online]. Available: http://www.usc.edu/dept/chepa/documents/publications/selection.pdf
Wiratchai, N. 1999. LISREL Model: Inferential Statistics for Research. 3rd ed. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing House. 111




No comments:
Post a Comment